Build a Modern Scalable System - Practice on Service Mesh Mode with Consul, Nomad and Envoy
This article is Part 6 in a 7-Part Series.
- Part 1 - Build a Modern Scalable System - Basics
- Part 2 - Build a Modern Scalable System - Runtime Challenges
- Part 3 - Build a Modern Scalable System - Practice on Embedded Router Mode w/ Spring-Cloud
- Part 4 - Build a Modern Scalable System - Practice on Gateway Mode For Mixed-Languages Case
- Part 5 - Build a Modern Scalable System - Practice on Service Mesh Mode with Consul and Nomad
- Part 6 - This Article
- Part 7 - Build a Modern Scalable System - Presentation of Runtime and Data Layers Challenges(in Chinese)
Table of Contents
In last post, I introduced the service mesh mode via a PoC sample with consult connect, it's builtin proxy and nomad. This post will focus on the PoC sample for service mesh mode with envoy proxy, which will provide a production grade solution for a mixed languages development challenges in MSA.
All of the sample source code is hosted on repsoitry, To simplify the sample content, I did not introduce envoy compilation in this sample context, you should follow the envoy developer guide to build out a envoy binary to run the sample, and also, if you are interested in aggregated logging, performance analysis, please refer to earlier posts.
Recall the service mesh mode
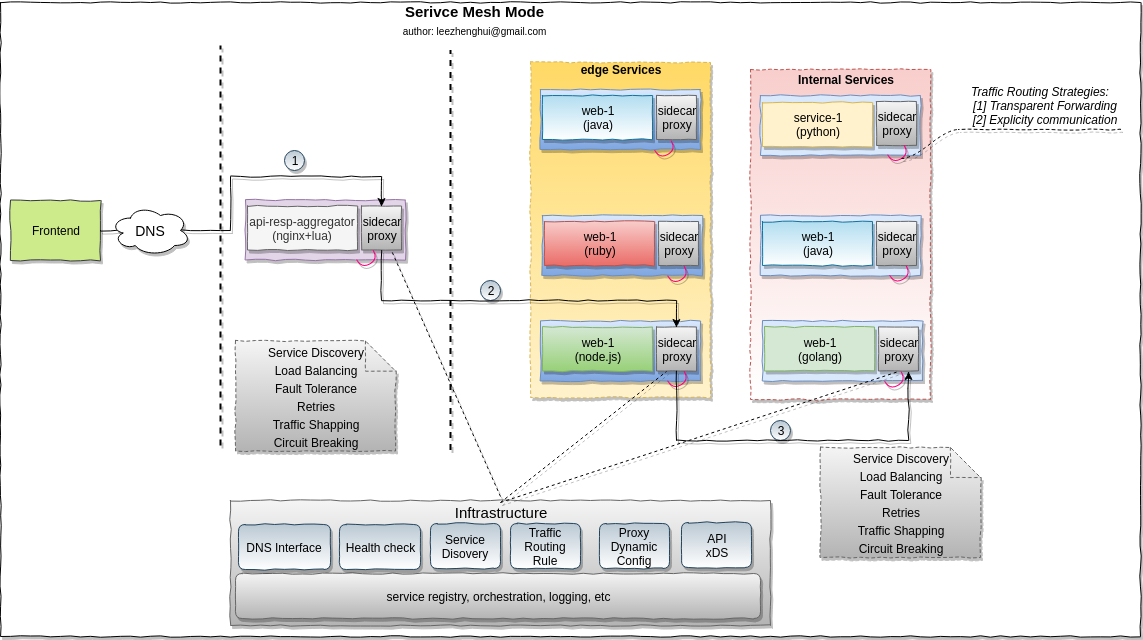
Please refer to my early post reference-modes-for-msa-service-communication for more details about the MSA runtime challenges.
PoC sample
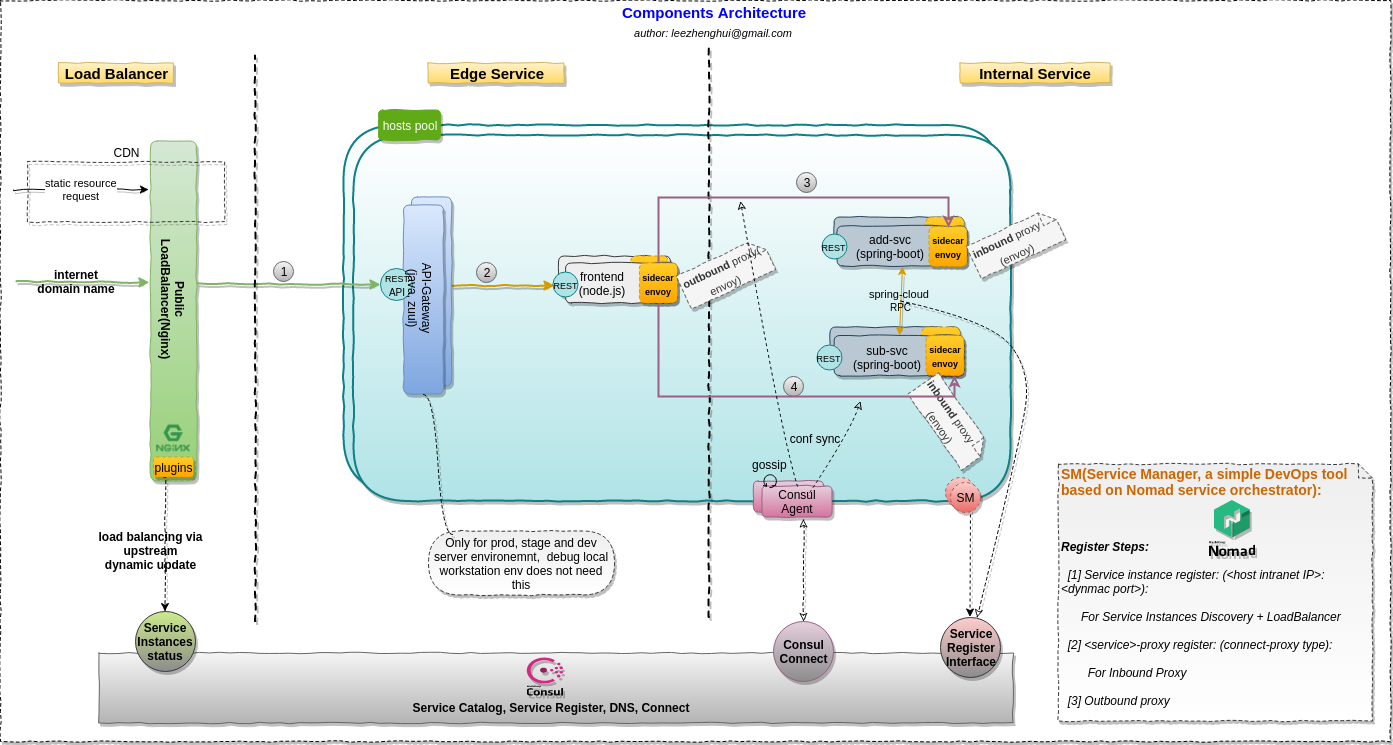
Scenario overview
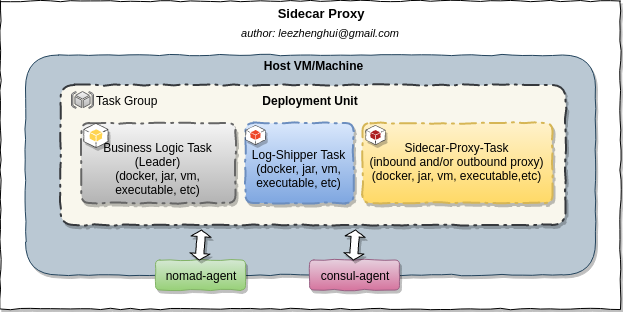
Sidecar Tasks
The sample is based on
consul connectand it's builtin proxy for the serviemesh. We want to use it to demonsrate the service mesh concepts for a hybrid environments(docker is not the only packing method, mixed deployable types for the service orchestration which could not be achieved by k8s only. cloud-native and on-premise co-exists). Please note, Consule connect was introduced in Consul 1.2 and be marked as beta quality for now, thus, not ready to be used in a production environment.
Soruce code structure
Modules
├── modules
│ ├── add.svc // add operator service, which will be called by calculator-ui
│ │ ├── build.gradle
│ │ ├── out
│ │ └── src
│ ├── api.gateway // api.gateway based on Zuul
│ │ ├── build.gradle
│ │ ├── out
│ │ └── src
│ ├── frontend // front-end service(edge service), which is implemeted by node.js, will call to add.svc and sub.svc
│ │ ├── build.gradle
│ │ ├── out
│ │ └── src
│ ├── ifw.lib // A prototype simple library impl to demonstrate an AOP based invocation framework with annotated QoS supports (just for demo only, not a production quality)
│ │ ├── build.gradle
│ │ ├── out
│ │ └── src
│ ├── sub.svc // subtract operator service, which will be called by calculator-ui
│ │ ├── build.gradle
│ │ ├── out
│ │ └── src
Operational source code
ops
├── Vagrantfile // Vagrant file
├── ansible // ansible scripts for install and start services, including: commoent runtime dependences, zookeeper, kafka, nginx(for local pkgs repo), install JVM, filebeat, consul, nomad, elasticsearch, logstash, kibana and wrk
├── bin // script, including boostrap.sh, click.sh(fire an invocation on the sample), kafka-*-monitor.sh, start_all_jobs.sh and stop_all_jobs.sh
├── deployable // nomad job definition files(hcl) for microservices
├── deps // binary dependences, which cache it locally to reduce(avoid) network deps during demonstration
├── dist // pkgs publish folder, nginx is started on this folder to simulate a pkg repository
├── sidecar-register // So far, nomad still not support sidecar service definition in it's serivce stanza, so we need to register it by ourself and startup the envoy instance by a seperate task.
As nomad still not support to define a service with sidecar_service in the task, for the time being, we use separate nomad job to declare sidecar service and bootstrap envoy.
Quick Start with Helloworld Sample(TCP Echo)
Before we get to the PoC sample, let's get a quick start on a simple tcp echo sample to help getting familiar with the consul connect envoy command, and unerstand what exactly it does under the hood.
- Prerequisites
- Envoy executable binary(following the guide for a developer build)
- socat is installed
-
Launch a TCP echo server with socat
socat -v tcp-l:9090,fork exec:"/bin/cat" - Define consul config definitions to file "envoy_demo.hcl"
services { name = "client" port = 8080 connect { sidecar_service { proxy { upstreams { destination_name = "echo" local_bind_port = 9191 } } } } } services { name = "echo" port = 9090 connect { sidecar_service {} } } -
Dump consul service definitions
{ "client": { "ID": "client", "Service": "client", "Tags": [], "Meta": {}, "Port": 8080, "Address": "", "Weights": { "Passing": 1, "Warning": 1 }, "EnableTagOverride": false }, "client-sidecar-proxy": { "Kind": "connect-proxy", "ID": "client-sidecar-proxy", "Service": "client-sidecar-proxy", "Tags": [], "Meta": {}, "Port": 21000, "Address": "", "Weights": { "Passing": 1, "Warning": 1 }, "EnableTagOverride": false, "ProxyDestination": "client", "Proxy": { "DestinationServiceName": "client", "DestinationServiceID": "client", "LocalServiceAddress": "127.0.0.1", "LocalServicePort": 8080, "Upstreams": [ { "DestinationType": "service", "DestinationName": "echo", "LocalBindPort": 9191 } ] } }, "echo": { "ID": "echo", "Service": "echo", "Tags": [], "Meta": {}, "Port": 9090, "Address": "", "Weights": { "Passing": 1, "Warning": 1 }, "EnableTagOverride": false }, "echo-sidecar-proxy": { "Kind": "connect-proxy", "ID": "echo-sidecar-proxy", "Service": "echo-sidecar-proxy", "Tags": [], "Meta": {}, "Port": 21001, "Address": "", "Weights": { "Passing": 1, "Warning": 1 }, "EnableTagOverride": false, "ProxyDestination": "echo", "Proxy": { "DestinationServiceName": "echo", "DestinationServiceID": "echo", "LocalServiceAddress": "127.0.0.1", "LocalServicePort": 9090, "Upstreams": [] } } }As you can see, the
connect.sidecar_servicedefintion will be expanded out to a explicit service definition with typeconnect-proxyin consul. - Launch consul
cd /vagrant/deployable/ /opt/consul/bin/consul agent -dev --config-file ./envoy_demo.hcl -
Start envoy inbound and outbound proxies:
-
Inbound
/opt/consul/bin/consul connect envoy -sidecar-for echo -admin-bind localhost:19000 -bootstrap > ./bootstrap_echo.json /opt/envoy/bin/envoy --v2-config-only --config-path ./bootstrap_echo.json --disable-hot-restart -l debugAlternatively,
/opt/consul/bin/consul connect envoy -sidecar-for echo -admin-bind localhost:19000 -envoy-binary=/opt/envoy/bin/envoy -- -l debug- Outbound
/opt/consul/bin/consul connect envoy -sidecar-for client -admin-bind localhost:19001 -bootstrap > ./bootstrap_client.json /opt/envoy/bin/envoy --v2-config-only --config-path ./bootstrap_client.json --disable-hot-restart -l debugAlternatively,
/opt/consul/bin/consul connect envoy -sidecar-for client -admin-bind localhost:19001 -envoy-binary=/opt/envoy/bin/envoy -- -l debug
The
consule connectenvoy command actually launch envoy with two steps:[1] Generate a bootstrap config file for envoy
[2] Launch envoy with the generated bootstrap config
-
-
Run a client on
9191portnc 127.0.0.1 9191Input a string for a echo.
Run the PoC Sample
By the time of my writting the doc, envoy integration with nomad is still working in progress that’s far from being complete, and also, in nomad, the service stanza does not support connect sidecar_service definitions. so we do not have a easy way to enable dynamical port feature. In below sample, the ports assigned to frontend, add-svc and sub-svc are static, as a result, the services are running with single instance, no replicated service instances running for now.
Steps
- Prerequisites
- Java
- Node.js
- Gradle
- Envoy executable binary(following the guide for a developer build)
-
Git clone the project
On host:
git clone git@github.com:leezhenghui/hello-servicemesh-envoy.git -
Gradle build/deploy distribution
On host:
cd hello-servicemesh-envoy/modules/frontend npm install cd ../../ gradle deploy -
Launch VM
On host:
cd ops vagrant up -
Provision the VM
On host:
vagrant provision -
Start all nomad jobs
On host:
vagrant sshIn VM
cd /vagrant/bin ./start_all_jobs.shIn addition to start the needed service, script register sidecar services and start envoy proxies under the hood.
-
sidecar services
{ "name": "add-svc-proxy", "kind": "connect-proxy", "proxy": { "destination_service_name": "add-svc", "local_service_address": "10.10.10.150", "local_service_port": 9090 }, "port": 21000 }{ "name": "sub-svc-proxy", "kind": "connect-proxy", "proxy": { "destination_service_name": "sub-svc", "local_service_address": "10.10.10.150", "local_service_port": 8080 }, "port": 21001 }{ "name": "add-svc-ref-proxy", "kind": "connect-proxy", "proxy": { "destination_service_name": "frontend", "local_service_address": "10.10.10.150", "local_service_port": 7070, "upstreams": [{ "destination_type": "service", "destination_name": "add-svc", "local_bind_address": "127.0.0.1", "local_bind_port": 9191 }] }, "port": 21002 }{ "name": "sub-svc-ref-proxy", "kind": "connect-proxy", "proxy": { "destination_service_name": "frontend", "local_service_address": "10.10.10.150", "local_service_port": 7070, "upstreams": [{ "destination_type": "service", "destination_name": "sub-svc", "local_bind_address": "127.0.0.1", "local_bind_port": 8181 }] }, "port": 21003 }- Bootstrap envoy proxies
consul connect envoy -sidecar-for add-svc -proxy-id add-svc-proxy -admin-bind localhost:19000 -envoy-binary=/opt/envoy/bin/envoy -- -l debug consul connect envoy -sidecar-for sub-svc -proxy-id sub-svc-proxy -admin-bind localhost:19001 -envoy-binary=/opt/envoy/bin/envoy -- -l debug consul connect envoy -sidecar-for frontend -proxy-id add-svc-ref-proxy -admin-bind localhost:19002 -envoy-binary=/opt/envoy/bin/envoy -- -l debug consul connect envoy -sidecar-for frontend -proxy-id sub-svc-ref-proxy -admin-bind localhost:19003 -envoy-binary=/opt/envoy/bin/envoy -- -l debug
-
-
Run the sample
In VM:
./click.sh -
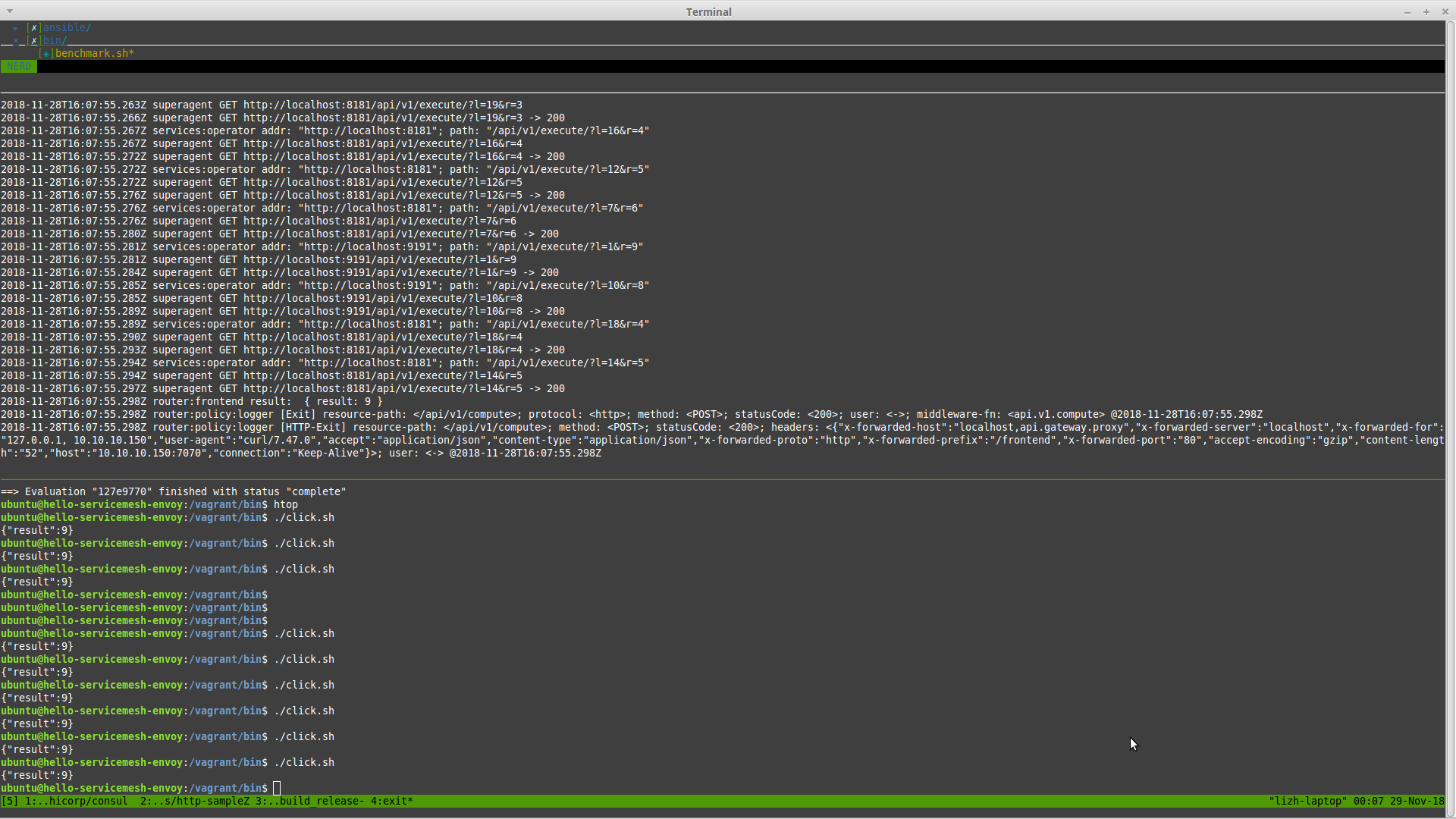
Run benchmark
In VM:
./benchmark.sh
Result of Service Discovery and Load Balance
Wrapping up
In this post, we introduce the service mesh mode with envoy proxy, this is the last post in this series for runtime challenges practices. From next post, we will start the data part challenges introduction and practices.
This article is Part 6 in a 7-Part Series.
- Part 1 - Build a Modern Scalable System - Basics
- Part 2 - Build a Modern Scalable System - Runtime Challenges
- Part 3 - Build a Modern Scalable System - Practice on Embedded Router Mode w/ Spring-Cloud
- Part 4 - Build a Modern Scalable System - Practice on Gateway Mode For Mixed-Languages Case
- Part 5 - Build a Modern Scalable System - Practice on Service Mesh Mode with Consul and Nomad
- Part 6 - This Article
- Part 7 - Build a Modern Scalable System - Presentation of Runtime and Data Layers Challenges(in Chinese)