Build a Modern Scalable System - Practice on Gateway Mode For Mixed-Languages Case
This article is Part 4 in a 7-Part Series.
- Part 1 - Build a Modern Scalable System - Basics
- Part 2 - Build a Modern Scalable System - Runtime Challenges
- Part 3 - Build a Modern Scalable System - Practice on Embedded Router Mode w/ Spring-Cloud
- Part 4 - This Article
- Part 5 - Build a Modern Scalable System - Practice on Service Mesh Mode with Consul and Nomad
- Part 6 - Build a Modern Scalable System - Practice on Service Mesh Mode with Consul, Nomad and Envoy
- Part 7 - Build a Modern Scalable System - Presentation of Runtime and Data Layers Challenges(in Chinese)
Table of Contents
- Table of Contents
- Recall the gateway mode
- PoC sample
- Load Balancer upstream dynamic update
- Run the Sample
- Wrapping up
In last post, I introduced the embedded router mode via spring-cloud PoC sample. This post will focus on the PoC sample for gateway mode, which can provide a solution for a mixed languages development challenges in MSA.
All of the sample source code is hosted on repsoitry, it is automated, and easy to run. To simplify the sample content, I just keep the gateway-mode related features in it, if you are interested in aggregated logging, performance analysis, please refer to earlier posts.
Recall the gateway mode
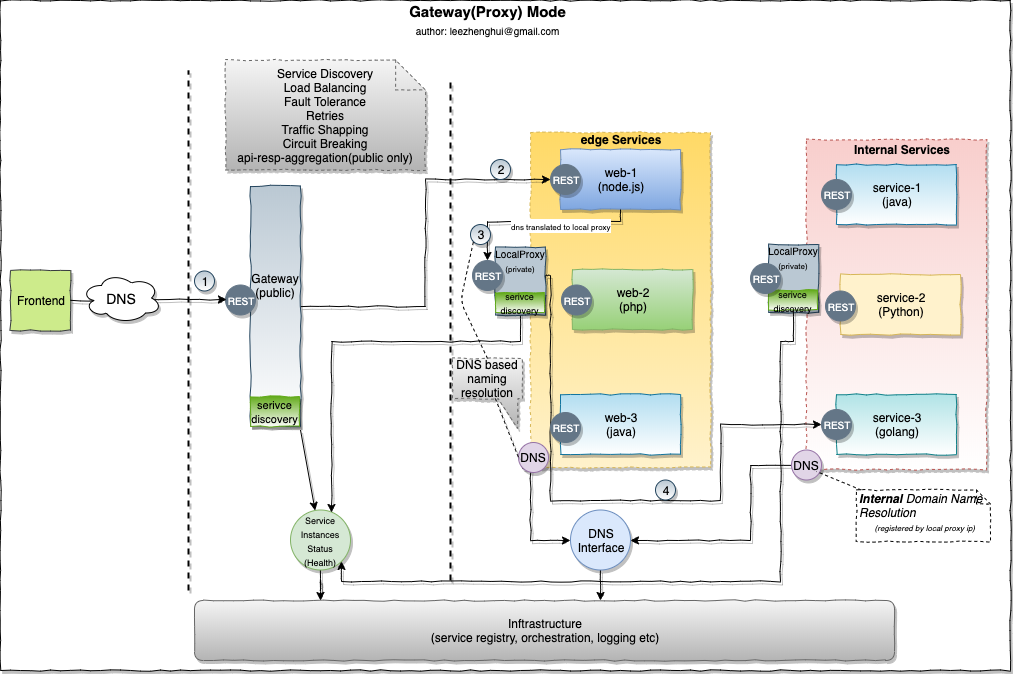
Please refer to my early post reference-modes-for-msa-service-communication for more details about the MSA runtime challenges.
PoC sample
Scenario overview
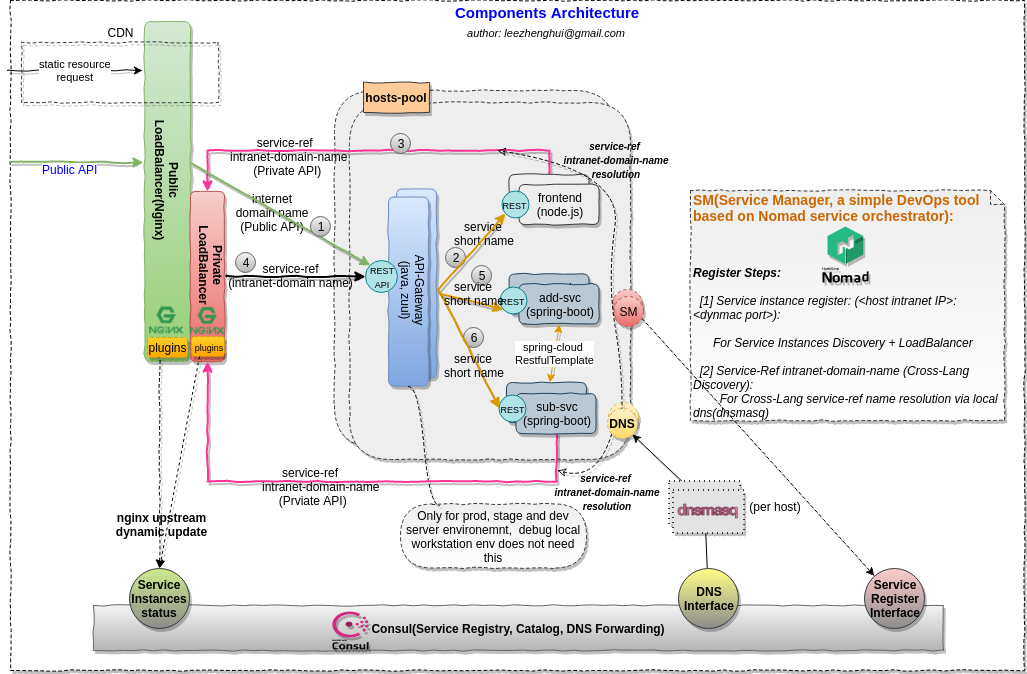
Soruce code structure
Modules
├── modules
│ ├── add.svc // add operator service, which will be called by calculator-ui
│ │ ├── build.gradle
│ │ ├── out
│ │ └── src
│ ├── api.gateway // api.gateway based on Zuul
│ │ ├── build.gradle
│ │ ├── out
│ │ └── src
│ ├── frontend // front-end service(edge service), which is implemeted by node.js, will call to add.svc and sub.svc
│ │ ├── build.gradle
│ │ ├── out
│ │ └── src
│ ├── ifw.lib // A prototype simple library impl to demonstrate an AOP based invocation framework with annotated QoS supports (just for demo only, not a production quality)
│ │ ├── build.gradle
│ │ ├── out
│ │ └── src
│ ├── sub.svc // subtract operator service, which will be called by calculator-ui
│ │ ├── build.gradle
│ │ ├── out
│ │ └── src
Operational source code
ops
├── Vagrantfile // Vagrant file
├── ansible // ansible scripts for install and start services, including: commoent runtime dependences, zookeeper, kafka, nginx(for local pkgs repo), install JVM, filebeat, consul, nomad, elasticsearch, logstash, kibana and wrk
├── bin // script, including boostrap.sh, click.sh(fire an invocation on the sample), kafka-*-monitor.sh, start_all_jobs.sh and stop_all_jobs.sh
├── deployable // nomad job definition files(hcl) for microservices
├── deps // binary dependences, which cache it locally to reduce(avoid) network deps during demonstration
├── dist // pkgs publish folder, nginx is started on this folder to simulate a pkg repository
└── svc-ref-register // internal domain name registry by service short name
Load Balancer upstream dynamic update
-
Nginx/HAProxy with Consul Template
- Nginx with Custom Module
- Dynamic Nginx Upstreams for Consul via lua-nginx-module by Zachary Schneider
- Nginx upsync module
- Nginx Pro DNS resolution
- ngx_http_set_backend which inspired binding Nginx modules in C to Consul in Golang
-
HAProxy 1.8
HAProxy 1.8 brings resolution for ports through SRV records and support for EDNS, making it pair perfectly with Consul.
Run the Sample
All of service instances are using dynamic ports in this sample to demonstrate the auto-scale features.
As we want to focus on servicemesh part in the sample, to make the verification(for service discovery and load balancing) ealier, only the internal services are scheduled multiple instances in this sample. If you are interested in the edge services, please refer to hello-msaproxy for details.
Steps
- Prerequisites
- Java
- Node.js
- Gradle
-
Git clone the project
On host:
git clone git@github.com:leezhenghui/hello-msaproxy.git -
Gradle build/deploy distribution
On host:
cd hello-msaproxy/modules/frontend npm install cd ../../ gradle deploy -
Launch VM
On host:
cd ops vagrant up -
Provision the VM
On host:
vagrant provision -
Start all nomad jobs
For each services, two intances will be created for a load balance, service discovery testing
On host:
vagrant sshIn VM
cd /vagrant/bin ./start_all_jobs.sh -
Run the sample
In VM:
./click.sh -
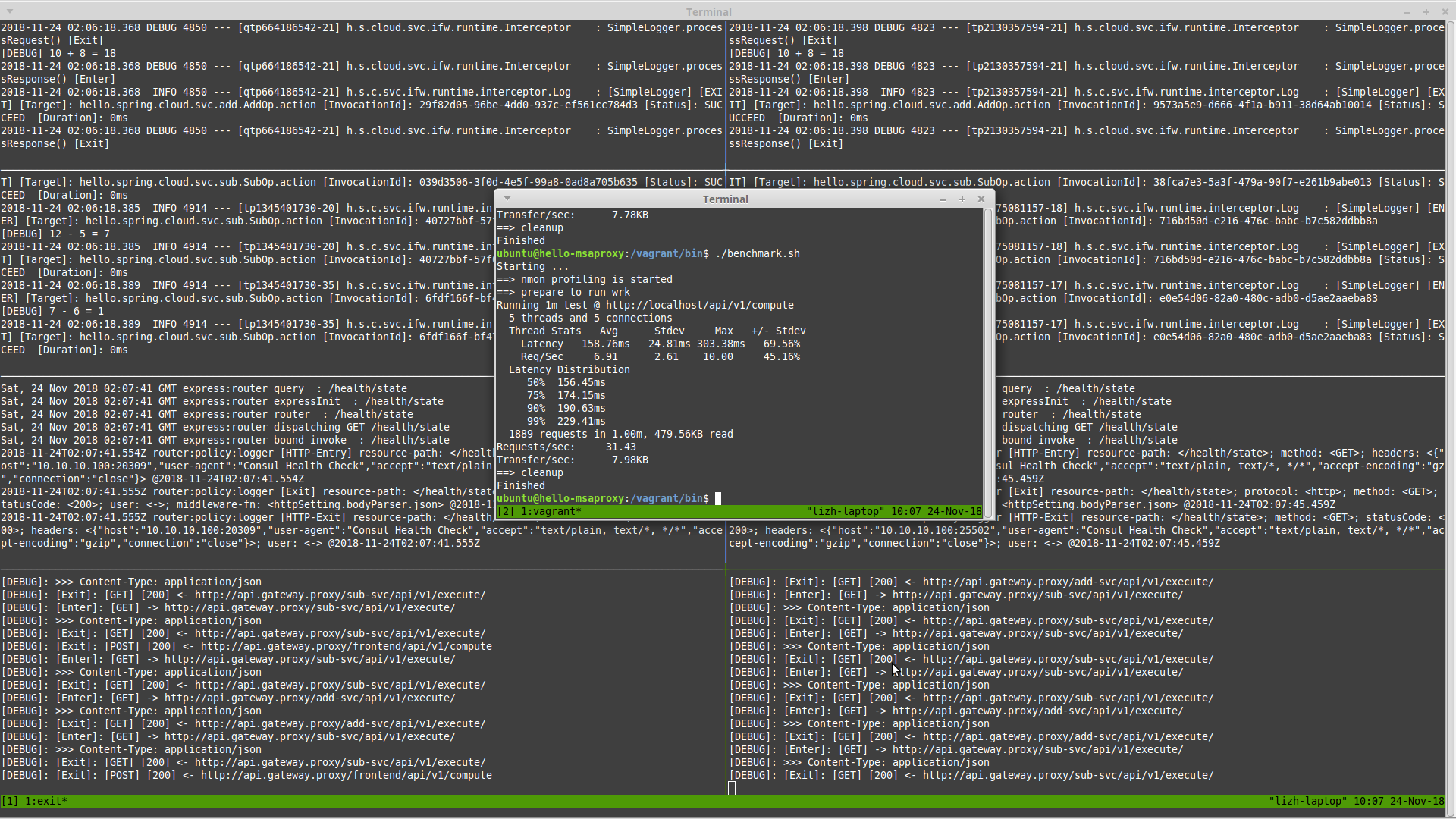
Run benchmark
In VM:
./benchmark.sh
Result of Service Discovery and Load Balance
Wrapping up
In this post, we introduce the gateway mode via PoC sample, in next post, we will take a hands-on practice on service mesh mode for a mixed programming language scenario.
This article is Part 4 in a 7-Part Series.
- Part 1 - Build a Modern Scalable System - Basics
- Part 2 - Build a Modern Scalable System - Runtime Challenges
- Part 3 - Build a Modern Scalable System - Practice on Embedded Router Mode w/ Spring-Cloud
- Part 4 - This Article
- Part 5 - Build a Modern Scalable System - Practice on Service Mesh Mode with Consul and Nomad
- Part 6 - Build a Modern Scalable System - Practice on Service Mesh Mode with Consul, Nomad and Envoy
- Part 7 - Build a Modern Scalable System - Presentation of Runtime and Data Layers Challenges(in Chinese)